Consultivo Blog | Social & Sustainability | BRSR Reasonable Assurance

Reasonable Assurance in BRSR Core is a mandatory requirement in India for the top 150 companies on a net worth basis, as mandated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) for FY 2023-24.
Considering the complex landscape of Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR), attaining clarity and reasonable assurance is paramount for business leaders.
What you will find here
Unraveling the Significance of BRSR Reasonable Assurance – The Context
In this comprehensive guide, we unveil the essentials of reasonable assurance in BRSR, demystifying its significance and impact.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional or new to the domain of BRSR, understanding reasonable assurance is pivotal in navigating the evolving reporting standards.
With a focus on transparency and accountability, this article dissects the practical implications of reasonable assurance. It will also provide actionable insights that resonate with the diversifying needs of modern businesses.
We will guide you in comprehending the intricacies of reasonable assurance. This knowledge empowers business leaders to precisely align their BRSR strategies, ensuring regulatory compliance and bolstering trust among stakeholders.
Get ready to embark on a journey that transforms the complex into the comprehensible, unlocking the true potential of reasonable assurance in BRSR Core for every visionary business leader.
A 2023 survey in India found that 75% of Indian companies are planning to hire external consultants to help them implement the BRSR CORE framework.
Beginning the Assurance Story – The Introduction
Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) is a rapidly evolving field, with increasing scrutiny from regulators, investors, and other stakeholders. In India, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has mandated that the top 150 listed companies must obtain reasonable assurance on their BRSR Core disclosures from FY 2023-24 onwards.
Value of transparent reporting in BRSR and Stakeholder Communication
Transparent reporting is the disclosure of accurate and complete information about a company’s operations, financial performance, and sustainability impacts.
It is essential for building lasting relationships with investors, customers, employees, and the community at large.
Effective and transparent communication is at the heart of any sustainability or ESG report and it brings many values to the organisation:
BRSR reasonable assurance – value for investors
Investors want to invest in companies that are transparent and accountable. They need to be able to trust that the information that companies disclose is accurate and complete in order to make informed investment decisions.
Transparent reporting helps investors assess the risks and opportunities associated with investing in a company, and it makes it easier for them to track a company’s progress over time.
Reasonable assurance in BRSR – value for customers
Customers want to buy products and services from companies that they trust. Transparent reporting helps customers understand the company’s values, its commitment to sustainability, and its ethical practices.
This information can help customers to make informed purchasing decisions and to build stronger relationships with the companies that they support
Value for employees
Employees want to work for companies that are transparent and accountable. They want to be able to trust that their employer is acting in their best interests and that it is committed to creating a sustainable future.
Transparent reporting helps employees understand the company’s goals and objectives, its financial health, and its social and environmental impacts.
This information can help employees to feel more engaged in their work and to be more productive
Value for the community at large
The community at large wants to support companies that are good corporate citizens.
Transparent reporting helps the community to understand the company’s impact on the local economy, the environment, and society as a whole.
This information can help the community to build stronger relationships with the companies that operate in their area.
Here are some specific examples of how transparent reporting can help companies to build lasting relationships with their stakeholders:
Increased investor confidence in BRSR Reasonable Assurance
Transparent reporting can help companies to attract and retain investors by increasing their confidence in the company’s management and its ability to deliver on its promises.
Improved customer loyalty
Transparent reporting can help companies to build stronger relationships with their customers by demonstrating their commitment to sustainability, transparency, and accountability.
Enhanced employee engagement
Transparent reporting can help companies to improve employee engagement by giving employees a better understanding of the company’s goals and objectives, its financial health, and its social and environmental impacts.
Strengthened community relationships
Transparent reporting can help companies to build stronger relationships with the communities in which they operate by demonstrating their commitment to corporate social responsibility and sustainable development.
Overall, transparent reporting is essential for building lasting relationships with investors, customers, employees, and the community at large. It is a key component of good corporate governance and sustainable business practices.
Transparency, BRSR Reasonable Assurance and ESG
Transparency embodies the level of openness and honesty that a company exhibits when communicating its ESG risks and opportunities to investors, stakeholders, and the public. In the fast-evolving world of business, the demand for transparency and sustainability has never been more pronounced. Today’s stakeholders, from investors to consumers, are increasingly scrutinizing companies’ practices and performance when it comes to Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR).
The intricate relationship among Transparency, BRSR and ESG is also crucial.
BRSR mandates that companies disclose their ESG performance and impact in a comprehensive, uniform, and transparent manner.
This standardized reporting format not only enhances the quality and comparability of ESG information but also aligns Indian businesses with global best practices and standards.
It’s all about commitment
By embracing BRSR, companies demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and business responsibility while effectively conveying their value proposition to an increasingly ESG-conscious audience of investors and stakeholders.
Furthermore, BRSR inspires businesses to adopt a holistic and strategic approach to ESG management, seamlessly integrating sustainability into their core operations and decision-making processes. This synergy among BRSR, ESG, and Transparency marks a pivotal shift toward a more responsible, accountable, and sustainable corporate landscape in India.
A reasonable assurance in BRSR enhances transparency and investor confidence.
BRSR reasonable assurance meaning
Reasonable assurance is an independent assessment by a qualified third-party assurance provider that a company’s BRSR disclosures are accurate and complete. It provides stakeholders with confidence in the credibility and transparency of a company’s BRSR performance.
On the other hand, BRSR Reasonable assurance meaning does not imply absolute assurance, as there is always some inherent risk of error or fraud in any reporting process.
However, it does imply that the auditor has performed sufficient procedures to obtain reasonable confidence that the information is free from material misstatement.
Importance of BRSR or ESG Reasonable Assurance
Reasonable assurance is more than just a regulatory requirement; it’s a cornerstone of trust-building.
This section elaborates on the significance of reasonable assurance in BRSR, explaining how it enhances credibility, transparency, and accountability.
Business leaders should recognize its pivotal role in maintaining stakeholder trust and making informed decisions.
Benefits of BRSR Reasonable Assurance
Reasonable assurance offers a number of benefits to organizations, including:
- Enhanced credibility and transparency: Reasonable assurance signals to stakeholders that a company is committed to sustainability and transparency. This can lead to improved investor relations, customer loyalty, and employee engagement.
- Reduced risk of greenwashing: Reasonable assurance helps to ensure that a company’s BRSR disclosures are not misleading or unsubstantiated. This can reduce the risk of greenwashing allegations and reputational damage.
- Improved business resilience: By tracking and measuring their ESG performance, companies can identify and mitigate risks, improve operational efficiency, and create new opportunities.
Different Types of ESG Assurances: What Else is There?
When it comes to Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR), reasonable assurance is just one part of the broader landscape of assurances. While reasonable assurance ensures a high level of confidence in the accuracy of reported data, there are other types of assurances that play distinct roles in enhancing transparency and accountability.
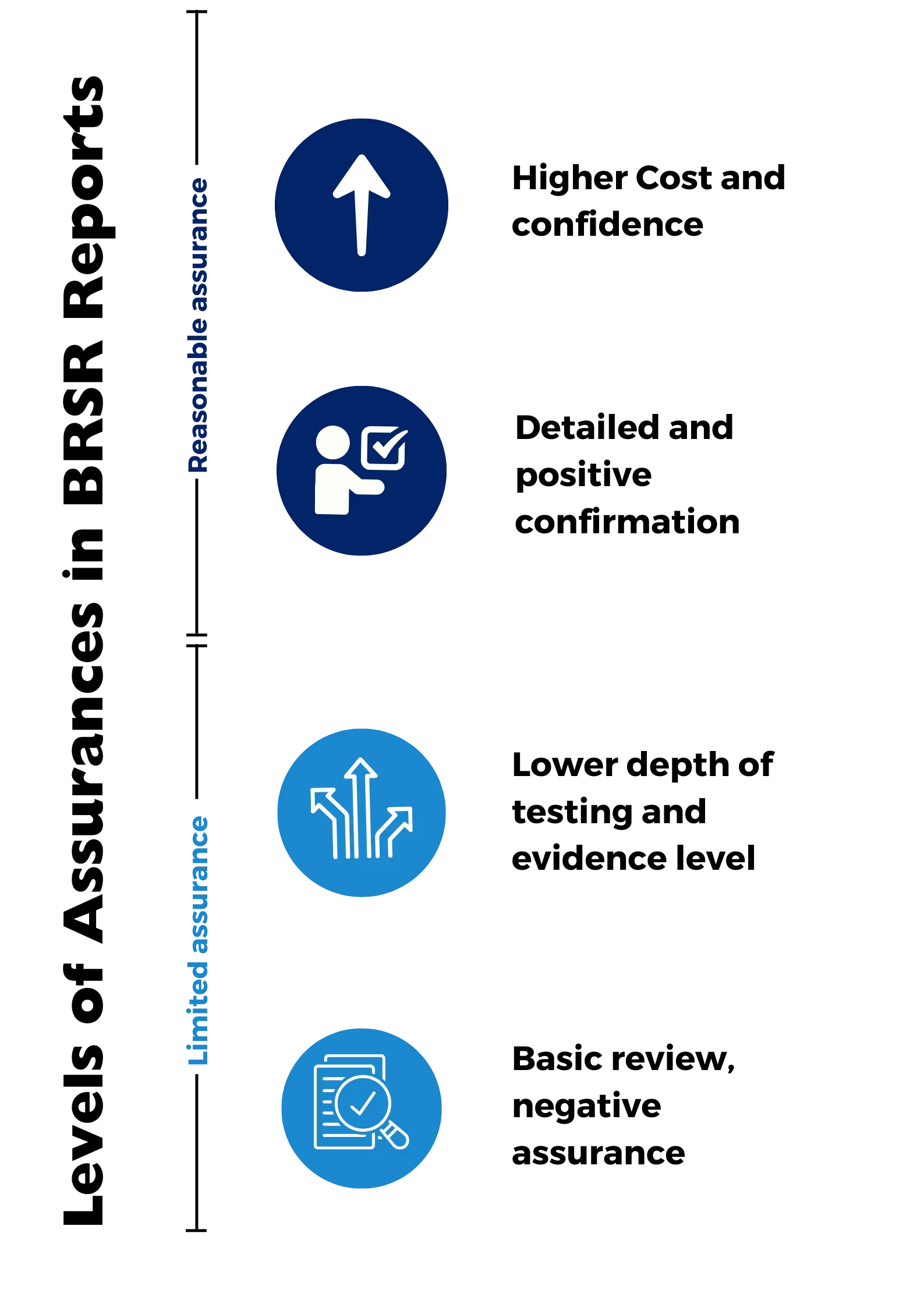
Limited assurance: It involves a lesser degree of testing and scrutiny compared to reasonable assurance. Limited assurance is often chosen when a company wishes to provide a level of assurance to stakeholders, but not as comprehensive or costly as reasonable assurance. It serves as a middle ground between no assurance and full assurance.
Another type is positive assurance, which involves an explicit statement that the reported information is accurate and free from material misstatements. This type of assurance is more assertive and affirmative in its nature, offering stakeholders a high level of confidence in the accuracy and completeness of the data.
Conversely, negative assurance involves a statement that nothing has come to the assurance provider’s attention that suggests the reported information is inaccurate or incomplete. It’s a more cautious approach, indicating that there are no glaring issues, but it doesn’t explicitly confirm the accuracy of the data.
How do you choose a type of assurance?
If you are a stock exchange listed company in India, then your choice of assurance type is guided by SEBI.
Other companies may choose the type of assurance that best aligns with their objectives and the level of confidence they wish to provide to stakeholders.
The selection of assurance type often depends on factors like the company’s size, industry, and the expectations of its investors and stakeholders.
These various types of assurances, including reasonable assurance, play vital roles in promoting transparency, accountability, and sustainability in the corporate world.
What Types of ESG or Sustainability Assurance Standards Exist other than BRSR?
In addition to BRSR, there are a number of emerging assurance standards that are being developed globally. These standards play an increasingly important role in ensuring the credibility and transparency of ESG disclosures in the future.
Here are some examples of emerging ESG or Sustainability assurance standards:
- The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Assurance Standard is a new standard that is designed to provide assurance on BRSR disclosures in accordance with the GRI Reporting Standards.
- The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) Assurance Standard is a new standard that is being developed to provide assurance on BRSR disclosures in accordance with the ISSB Sustainability Reporting Standards.
- The Assurance Standard for Sustainability Reporting (ASRS) is a new standard that has been developed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) to provide assurance on BRSR disclosures in accordance with a variety of sustainability reporting frameworks.
These emerging standards are expected to play a significant role in raising the quality and reliability of ESG or Sustainability assurance in the future.
Difference between ESG or BRSR Reasonable Assurance and Limited Assurance
Reasonable assurance and limited assurance are two different levels of assurance that can be provided on a company’s BRSR disclosures.
Reasonable assurance provides a higher level of assurance than limited assurance. It involves a more in-depth review of the company’s BRSR disclosures, including its data collection and reporting procedures, internal controls, and supporting documentation.
Limited assurance involves a less in-depth review of the company’s BRSR disclosures. It is typically provided when the company is not yet able to meet the requirements for reasonable assurance.
Reasonable assurance is a high but not absolute level of assurance, in which the auditor affirms that the information reported is materially correct. This means that the auditor has obtained sufficient and appropriate evidence to reduce the risk of material misstatement to an acceptably low level.
Reasonable assurance is usually expressed in a positive form, such as “in our opinion, the ESG/BRSR data and statements present fairly, in all material respects, the ESG/BRSR performance of the entity”.
Limited assurance is a lower level of assurance, in which the auditor states that nothing has come to their attention that causes them to believe that the information reported is materially misstated.
This means that the auditor has performed less extensive procedures than in a reasonable assurance engagement, but enough to obtain a meaningful level of assurance.
Limited assurance is usually expressed in a negative form, such as “based on our review, nothing has come to our attention that causes us to believe that the ESG/BRSR data and statements are not prepared, in all material respects, in accordance with the applicable ESG/BRSR performance reporting framework”.
The main differences between reasonable assurance and limited assurance are:
- The depth of testing: Limited assurance involves fewer tests of control focused on the information and underlying data, while reasonable assurance involves more comprehensive tests of control, systems, and processes.
- The level of evidence: Limited assurance gathers sufficient appropriate evidence, though it is deliberately limited, while reasonable assurance gathers more persuasive evidence.
- The cost of the engagement: Limited assurance is usually less costly and time-consuming than reasonable assurance, as it requires less work and resources.
- The level of confidence: Limited assurance provides a lower level of confidence than reasonable assurance, as it is based on a smaller sample size and test coverage.
Challenges Organizations May Face While Being Audited by a Third Party for BRSR or ESG Reasonable Assurance
The road to reasonable assurance is not without its obstacles.
In this section, we discuss the common challenges businesses face when striving for reasonable assurance. Identifying these challenges is the first step in overcoming them.
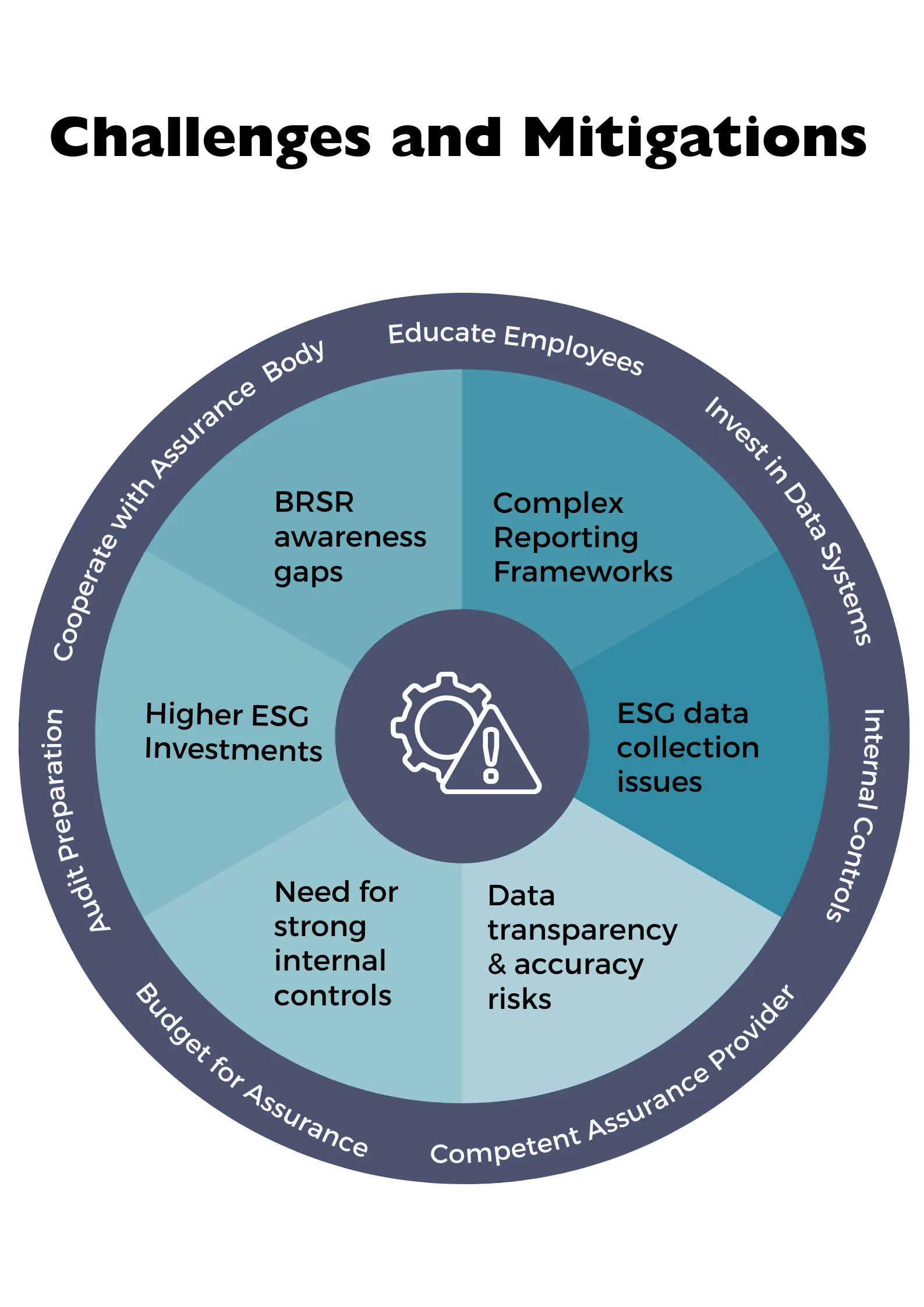
Lack of awareness and understanding of BRSR
Many companies and their key decision makers are not fully aware of what BRSR is or the requirements for achieving reasonable assurance.
Complex and evolving reporting frameworks
BRSR reporting frameworks can be complex and time-consuming to comply with. They are also constantly evolving, which can make it difficult for companies to keep up
Data collection and reporting challenges
Collecting and reporting accurate and timely ESG data can be challenging for companies, especially those with large and complex operations.
- Data transparency: The company may need to disclose sensitive financial and non-financial data to the third-party assurance provider. This could pose a risk to the company’s intellectual property or competitive advantage.
- Data accuracy: The third-party assurance provider may identify errors or inaccuracies in the company’s BRSR disclosures. This could lead to reputational damage or regulatory scrutiny.
- Data unavailability: The company may not have all of the data required for the third-party assurance provider to complete its review. This could delay the assurance process or result in a qualified opinion.
Internal controls
Companies need to have robust internal controls in place over ESG data collection and reporting in order to achieve reasonable assurance.
Cost of implementation of sustainability practices
They may include capital expenditures, operational expenses, staff training, and assurance fees.
Cost of BRSR Reasonable Assurance
The cost of obtaining reasonable assurance on BRSR Core disclosures can be significant, especially for smaller companies.
Mitigating the Challenges
Organizations can mitigate the risks associated with third-party assurance by taking the following steps:
- Educate your employees about BRSR. Make sure that your employees understand what BRSR is and the importance of achieving reasonable assurance.
- Select the right reporting framework. Choose a reporting framework that is appropriate for your company’s size, industry, and ESG performance.
- Invest in data collection and reporting systems. Implement systems and processes to help you collect and report ESG data in an accurate and timely manner.
- Develop strong internal controls. Develop and implement internal controls over ESG data collection and reporting.
- Budget for assurance. Factor the cost of assurance into your BRSR budget. Select a qualified and reputable assurance provider: The assurance provider should have the necessary expertise in ESG assurance and be independent of the company.
- Prepare for the assurance process: The company should gather all of the necessary data and documentation in advance of the audit. It should also identify any areas of potential risk and develop mitigation strategies.
- Cooperate fully with the assurance provider: The company should provide the assurance provider with timely access to all of the requested data and documentation. It should also respond promptly to any questions or concerns raised by the assurance provider.
The Role of Business Leaders in Ensuring Reasonable Assurance
Leadership is vital in driving change and ensuring compliance.
Here, we emphasise the role of business leaders in overseeing BRSR reasonable assurance or ESG Assurance process, setting the tone for the organisation, and aligning BRSR strategies with corporate goals.
Unlocking the true potential of reasonable assurance in BRSR for every visionary business leader.
Steps to Achieve Reasonable Assurance in BRSR
Implementing Reasonable Assurance in BRSR: Achieving accuracy and compliance in Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) requires a systematic process.
It begins with a deep understanding of the BRSR framework set by authorities like SEBI, including reporting standards and guidelines. The process involves:
- Scope and Materiality Assessment: Identifying material issues relevant to the organisation and stakeholders.
- Data Collection and Documentation: Gathering and systematically documenting relevant BRSR data.
- Data Verification and Risk Assessment: Implementing robust data verification processes, including internal and external audits, and assessing risks for potential misstatements or errors.
- Engagement with Assurance Providers: Organisations may engage internal or external experts specialising in sustainability reporting assurance.
- Detailed Assurance Planning and Execution: Developing and executing a comprehensive assurance plan, involving substantive testing, analytical procedures, and reassessing materiality.
- Reporting and Management Response: Preparing an assurance report detailing findings, followed by management’s response to address issues and implement corrective actions.
- Final Report Preparation and Review: Merging the assurance report with the BRSR report, ensuring alignment with BRSR requirements.
- Disclosure and Continuous Improvement: Publishing the report for stakeholder access and using insights from the process for future enhancements.
- Best Practices for Effective Integration: Early commencement, senior management buy-in, stakeholder communication, using the process for improvement, investing in training, establishing robust governance, selecting qualified assurance providers, and implementing their recommendations are crucial for successful BRSR or ESG reasonable assurance.
- Training and Resources for Business Leaders: Understanding BRSR is essential for business leaders. Training should be mandatory, tailored to business needs, and utilize various methods. Access to resources like GRI, SASB, and ISSB standards, along with ongoing learning opportunities, is vital for effective BRSR implementation.
The top reasons why Indian companies are not obtaining reasonable assurance on their BRSR disclosures are the lack of awareness about the BRSR framework, lack of a formal BRSR framework, the complexity of the framework, data quality issues, cost of implementation, and the cost of assurance.
How can I choose a qualified and independent assurance provider?
Choosing a qualified and independent assurance provider is an important decision for any entity that wants to report its business responsibility and sustainability performance in accordance with the BRSR Core framework.
The BRSR Core framework is an enforcement by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) to encourage listed entities to disclose their environmental, social and governance (ESG) practices and impacts along their value chain.
According to the SEBI circular dated July 12, 2023, the BRSR Core assurance provider should meet the following criteria:
- The assurance provider should be an independent party, meaning that it should not have any direct or indirect relationship with the entity or its group entities that could impair its objectivity or professional judgment.
- The assurance provider should have the necessary expertise and experience in conducting assurance engagements on ESG information, as well as relevant industry knowledge and understanding of the applicable reporting framework and standards.
- The assurance provider should not have any conflict of interest with the entity or its group entities, such as selling products or services, providing non-audit or non-assurance-related services, or having any financial or personal interest in the entity’s performance or outcomes.
- The assurance provider should follow the applicable assurance standards and guidelines, such as the International Standard on Assurance Engagements (ISAE) 3000 or the International Federation of Accountants (IFAC) Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants.
The SEBI circular dated July 12, 2023 also clarifies that the internal auditor of the entity or its group entities cannot be appointed as the BRSR Core assurance provider, as they do not meet the independence criteria.
To choose a qualified and independent assurance provider, the entity’s board of directors should evaluate the credentials and reputation of the potential candidates, as well as their approach and methodology for conducting the BRSR or ESG assurance engagement.
The board should also consider the cost and time involved in the assurance process, as well as the level of assurance expected by the stakeholders.
A 2023 study in India found that 68% of top 1000 (by market capitalization) Indian companies are aware of the BRSR CORE framework, but only 32% are prepared to comply with it in the first phase.

Let's discuss
Final Summary,
So, what are the key takeaways? It’s important to embrace and emphasize the process of reasonable assurance for BRSR success.
Reasonable assurance is an essential tool for organisations that are committed to sustainability and transparency. It provides stakeholders with confidence in the credibility and accuracy of a company’s BRSR disclosures.
By understanding the risks and benefits of reasonable assurance audit, and by taking the necessary steps to mitigate the risks, organisations can ensure that the assurance process is a positive experience that leads to enhanced value for all stakeholders.
We reiterate the benefits, challenges, and best practices discussed throughout the article, leaving business leaders inspired to elevate their BRSR game.
By the end of this comprehensive guide, you’ll have a profound understanding of reasonable assurance in BRSR, empowering you to navigate the complex landscape with confidence and clarity.
So, let’s get started on this enlightening journey, and unlock the true potential of Reasonable Assurance in ESG or BRSR for every visionary business leader.
Share this post
About the author
Director – Sustainable solutions at Consultivo
Madhabi Guha specialises in the domains of ESG, Social Compliance, Business and Human Rights, Development Projects and focuses on supporting go-to-market teams along with customer and partner relationships. Madhabi has been working in the sustainability & business excellence advisory business for over 15 years.
Madhabi has been developing individuals, teams, and organisations in the areas of leadership, excellence and Human Factors in the field of sustainability, people and community.
Related insights
Blogs
Knowledge Bank
Knowledge Bank
Knowledge Bank
News & Events
News & Events
Blogs
Blogs
View more in Impact Stories | Blogs | Knowledge Bank | News and Events















